For our purposes I will propose 5 classes of data structures. These being the array, list, tree, hash, and graph.
Arrays
Arrays are one of the most basic data structures and are characterized by direct access to every element in the structure. It is easy to picture them as a line of numbered buckets where you can place an element into or remove an element from any bucket.
Lists
Lists are another very basic data structure. In a list each node has one of more connections to other nodes. Access to the list is only at one or both ends. From any given element you can access any element which you have a connection to. Here is an example of a simple list.
Trees
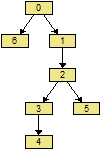
Trees are similar to lists in that each element has connections to other elements but in a tree the connections are more structured. Each element in a tree can have children. The number of children an element can have is an important property of a tree. The top element in a tree is called the root. The root in the only element which can be accessed externally. Any element with no children is called a leaf. An example of a binary tree might look like this.
Hashes
A hash is similar to an array but the elements are accessed according to a mathematical function.
Sometimes the elements in the hash will have lists coming form them.
Graphs
Unlike the other data structures graphs may or may not have much structure. We will get to these much later.
Each of these categories has many variants variants with different properties.
There are literally hundreds of different data structures and if you've never seen the one you need then you will never know when to use it. We will examine each of these categories in more detail with following posts.
Arrays
Arrays are one of the most basic data structures and are characterized by direct access to every element in the structure. It is easy to picture them as a line of numbered buckets where you can place an element into or remove an element from any bucket.
Lists
Lists are another very basic data structure. In a list each node has one of more connections to other nodes. Access to the list is only at one or both ends. From any given element you can access any element which you have a connection to. Here is an example of a simple list.
Trees
Trees are similar to lists in that each element has connections to other elements but in a tree the connections are more structured. Each element in a tree can have children. The number of children an element can have is an important property of a tree. The top element in a tree is called the root. The root in the only element which can be accessed externally. Any element with no children is called a leaf. An example of a binary tree might look like this.
Hashes
A hash is similar to an array but the elements are accessed according to a mathematical function.
Sometimes the elements in the hash will have lists coming form them.
Graphs
Unlike the other data structures graphs may or may not have much structure. We will get to these much later.
Each of these categories has many variants variants with different properties.
There are literally hundreds of different data structures and if you've never seen the one you need then you will never know when to use it. We will examine each of these categories in more detail with following posts.




Comments
Post a Comment